node
组成
- ECMAScript
- Node模块API
运行js文件
node xxx
模块化开发
Node.js规定一个JavaScript文件就是一个模块,模块内部定义的变量和函数默认情况下在外部无法得到 模块内部可以使用exports对象进行成员导出, 使用require方法导入其他模块
js开发弊端
- 文件依赖
- 命名冲突
模块导出
// module.js
exports.add= (a,b) => a+b
// 另外一种导出方式
module.exports.add = (a,b) => a+b;
// exports是module.exports的别名(地址引用关系),当它们指向的部署同一个对象时,导出对象最终以module.exports为准
模块导入
// other.js
let demo = require('./module');
demo.add(1,2);
系统模块
fs
const fs = require('fs')
// 读取文件
fs.readFile('./index.html',(err,doc)=>{
if (!err){
console.log(doc.toString())
}
})
// 文件写入
fs.writeFile('test.txt','run it',error => {
console.log(error);
})
path
const path = require('path')
// 拼接路径
console.log(path.join(__dirname,'TMP','MY')) // windows: C:\Users\MY\TMP\web\TMP\MY
// 大多数情况下使用绝对路径,因为相对路径有时候相对的是命令行工具的当前工作目录
第三方模块
npm install xx # 安装模块(本地安装)
npm uninstall xx # 卸载模块
npm install xx -g # 全局安装
nodemon
能监控文件的变化,变化时自动运行它
npm install nodemon -g # 安装
nodemon test # 使用nodemon代替node执行js文件,当js文件发生变更后,会自动重新运行js文件
nrm
npm下载地址切换工具
nrm ls # 列出可用源
nrm use xx # 使用某个源
gulp
npm install gulp
npm install gulp-cli -g
// 执行 gulp first
const gulp = require('gulp');
gulp.task('first', () => {
return gulp.src('./src/index.html')
.pipe(gulp.dest('./dist'))
})
插件
- 使用
// 压缩html
const htmlmin = require('gulp-htmlmin')
gulp.task('htmlmin', () => {
return gulp.src('./src/*.html')
.pipe(htmlmin({collapseWhitespace:true}))
.pipe(gulp.dest('./dist'))
})
全局对象
- global
package.json
项目描述文件,记录了当前项目信息,例如项目名称、版本、作者、github地址、 当前项目依赖了哪些第三方模块等。
使用npm init -y命令生成。
- dependencies
- devDependencies
- package-lock.json
- 锁定包的版本
- 记录了包以及依赖的下载地址
script
"scripts": {
"test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
"build":"nodemon a.js"
}
npm run build
模块加载机制
// 如果模块后缀省略,先找同名JS文件再找同名JS文件夹
// 如果找到了同名文件夹,找文件夹中的index.js
// 如果文件夹中没有index.js就会去当前文件夹中的package.js文件中查找main选项中的入口文件
// 如果再找不到就抛出异常
require('./xx')
// Node.js会假设它是 系统模块
// Node.js会去node_ modules文件夹中
// 首先看是否有该名字的JS文件
// 再看是否有该名字的文件夹
// 如果是文件夹看里面是否有index.js
// 如果没有index.js查看 该文件夹中的package.json中的main选项确定模块入口文件
// 否则找不到报错
require('xx')
异步编程
- 同步api
- 会阻塞
- 从返回值拿执行结果
- 异步api
- 不会阻塞
- 从回调函数拿执行结果
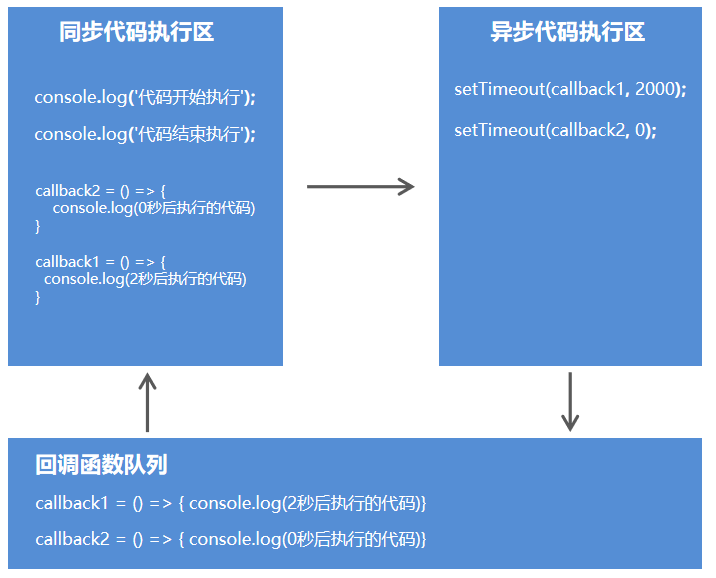
代码执行顺序
console.log('代码开始执行');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('2秒后执行的代码');
}, 2000);
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('"0秒"后执行的代码');
}, 0);
console.log('代码结束执行');
Promise
- 解决异步编程问题
Promise 是一个对象,它代表了一个异步操作的最终完成或者失败
var promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(function () {
let condition = true;
if (condition) {
resolve('foo'); // 回调then里的函数
} else {
reject('error'); // 回调catch里的函数
}
}, 300);
});
promise
.then(value => { console.log(value); })
.catch(error => { console.log(error) })
- 解决回调地狱
promise
.then(v=>{
// 如果返回Promise,则这个promise是调用下一个then的promise
// 如果不是promise,则就是下一个then的回调函数参数v
return new Promise()
})
.then(v=>{
return new Promise()
})
all与race
// 所有任务都完成才返回结果
Promise.all([query(),query(),query()]).then(()=>console.log('all mission complete'));
// 任一任务都完成就返回结果
Promise.race([query(),query(),query()]).then(()=>console.log('mission complete'));
错误捕获
Promise 对象的错误,会一直向后传递,直到被 onReject 函数处理或 catch 语句捕获为止
异步函数
// 使用async修饰,这个函数会返回一个Promise
const fn = async () => {};
async function fn () {}
async function f() {
return 11;
}
f()
.then(v=>console.log(v))
- await
await关键字只能出现在异步函数中
await关键字可暂停异步函数向下执行 直到promise返回结果
async function f1() {
return 11;
}
async function f2(){
return 22;
}
async function f(){
// 可以通过await关键字将异步函数转同步执行
let i1 = await f1();
let i2 = await f2();
console.log(i1,i2)
}
f()
一个被 async 修饰的函数会被包装为一个 Promise,遇到await关键字时,引擎会把该任务提交给微任务队列,然后暂停当前协程的执行,将主线程的控制权转交给父协程执行,同时会将await的这个对象返回给父协程,父协程拿到这个对象之后,就是调用then方法了
web服务器
创建
var http = require('http')
http.createServer((request,response)=>{
const body = "hello world";
response.writeHead(200,{
'Content-Length':Buffer.byteLength(body),
'Content-Type':'text/plain'
});
response.end(body);
}).listen(8888);
请求报文
const body = `request method:${request.method}
request url:${request.url}
request headers ua:${request.headers["user-agent"]}
`
响应报文
response.writeHead(200,{
'Content-Type':'application/json'
})
response.end('{"result":"25"}')
请求参数
- get
const url = require('url')
let { query } = url.parse(request.url, true)
// 输出name参数与age参数
response.end(query.name + "," + query.age)
- post
let postData = ''
request.on('data',params=>{
postData += params
})
request.on('end',()=>{
let i = querystring.parse(postData)
response.end(`name: ${i.name} address: ${i.address}`)
})
路由
let { pathname } = url.parse(req.url);
if (pathname == '/' || pathname == '/index') {
response.end('欢迎来到首页');
} else if (pathname == '/list') {
response.end('欢迎来到列表页页');
} else {
response.end('抱歉, 您访问的页面出游了');
}
静态资源
fs.readFile(__dirname+'/static'+pathname,(error,data)=>{
if (!error){
let type = pathname.substring(pathname.lastIndexOf('.')+1)
response.writeHead(200,{
"Content-Type":mime.getType(pathname)
})
response.end(data)
}else{
response.writeHead(404,{
"Content-Type":"text/html;charset=utf8"
})
response.end('404 NOT FOUND')
}
})